Generative artificial intelligence (AI) is poised to transform many industries in 2023. Powered by advances in deep learning and neural networks, generative AI allows computers to generate novel content like text, images, video, and audio that is indistinguishable from human-created works. While generative AI shows immense promise, it also poses challenging questions around ethics, legality, and societal impact that need to be thoughtfully considered.

This article provides an overview of the current state of generative AI, how it works on a technical level, examples of its applications across different domains, guidance on how to use it responsibly, and a look ahead at what the future may hold as this technology continues rapidly evolving.
Whether you're a business leader considering how to leverage generative AI, a policymaker determining how to govern it, or an everyday user trying to understand its capabilities, this article serves as an informative guide to the current landscape of generative AI in 2023.
What Is Generative AI?
Generative AI refers to machine learning models that are capable of generating new, synthetic content as their output. Unlike traditional AI systems which are focused on analysis or classification tasks, generative AI models create entirely new artifacts such as text, images, audio, video, and more. The key characteristic of generative AI is that it does not simply rearrange or transform existing content, but actually creates novel, original content based on patterns learned from training data.
Create Amazing Websites
With the best free page builder Elementor
Start NowSome of the most prominent examples of generative AI today include:
- Text generation models like GPT-3 which can write human-like text on a given prompt or topic.
- Image generation models such as DALL-E 2 which can create photorealistic images from text descriptions.
- Video generation models that can produce synthetic video clips based on textual narrative input.
- Audio generation for tasks like text-to-speech as well as generating music.
- 3D model generation using deep learning to design objects.
The training process for generative AI involves feeding the model a huge dataset related to the task at hand. For example, an image generation model would be trained on millions of images. The model then learns to recognize patterns and relationships between the training data through techniques like neural networks and deep learning. This allows it to generate brand new, realistic outputs similar to the training data when given a text or other input.
The key advantage of generative AI is its versatility and ability to augment human creativity. Possible use cases span content creation, design, problem solving, and more. However, it also comes with risks around data bias, misuse, and legality issues. Overall, generative AI represents an exciting new frontier in ML with immense potential.
Development Of Generative AI
Generative AI has progressed gradually, building upon previous advancements in the field of AI. Early on, machine learning enabled systems to learn and enhance themselves from experience without the need for explicit programming.
As machine learning techniques matured, neural networks emerged. Loosely modeled after the human brain, neural nets can digest huge datasets to become powerful tools for tasks like image recognition, natural language processing, and content creation.

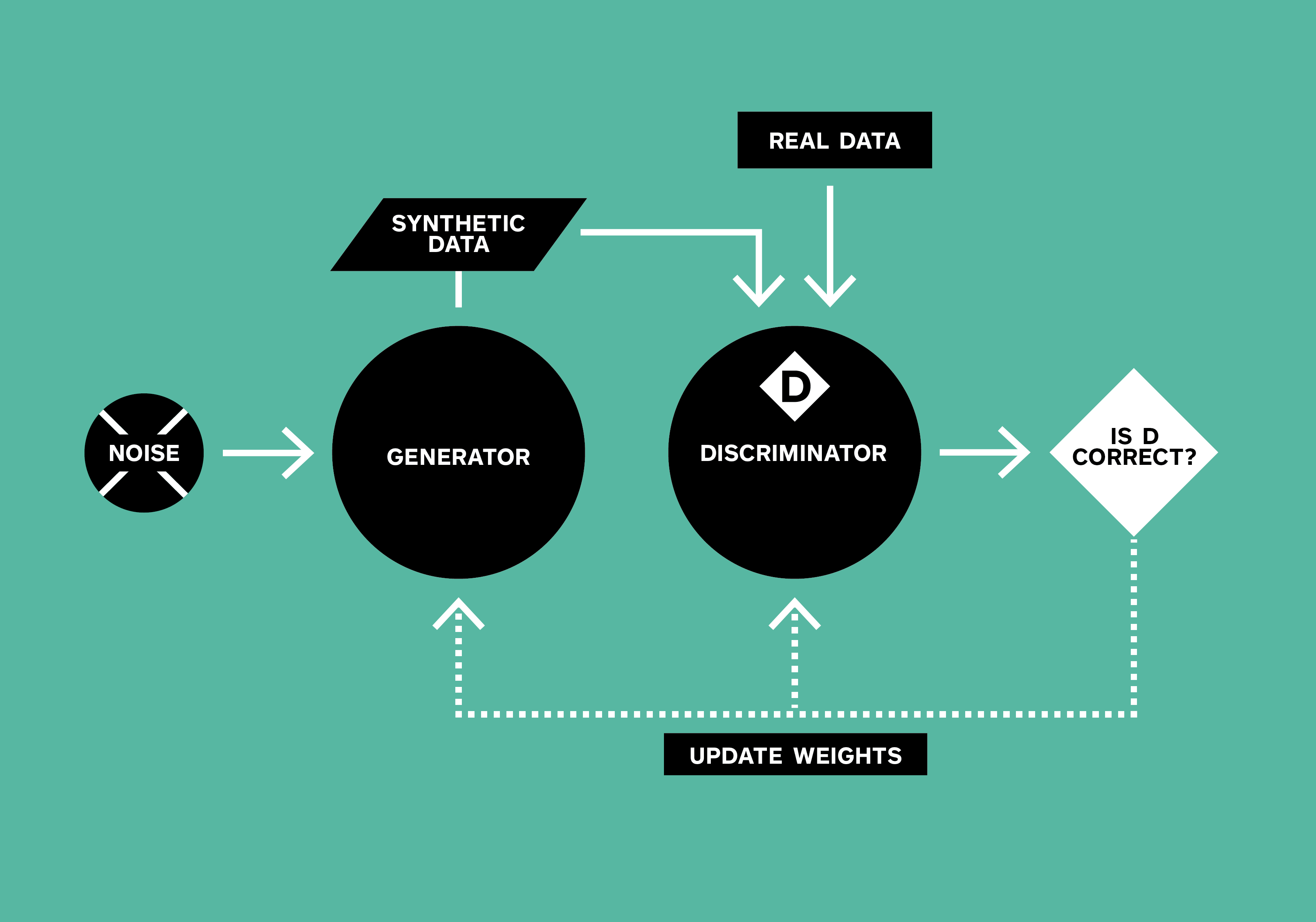
Generative AI took major steps forward with the invention of Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs). A GAN uses two competing components: a generator and a discriminator. The generator produces new synthetic outputs, while the discriminator analyzes them against real training data trying to identify fakes. This adversarial collaboration allows the generator to iteratively improve at creating increasingly realistic and human-like data.
With these and other innovations working behind the scenes, generative AI has crept into various consumer and business applications. From personalized recommendation systems to creative tools for writing, art, and music, the average person can now benefit from generative AI without needing expertise in the underlying technology.
In summary, progress in generative AI has been driven by key milestones in machine learning, neural networks, and GANs. As the technology continues rapidly advancing, it will unlock new creative potential while requiring thoughtful governance.
Application Of Generative AI
Language Processing & Writing
Generative AI is really changing the game when it comes to language processing and writing. Tools like ChatGPT (which uses the GPT-3 model) and Copy.ai are becoming indispensable for creating content, streamlining workflows, drafting emails and documents, writing articles, and answering questions. These tools can dramatically boost productivity and creativity.
Through our research on artificial intelligence writing and natural language processing (NLP), we've found some of the best tools that leverage these text-based AI models. These include:
- AI writing assistants and software that help with drafting, editing, rewriting, and more
- AI paraphrasing and summarizing tools that rephrase text more naturally
- AI chatbots for customer service, sales, and other conversations
- AI content and plagiarism checkers that scan for duplicates
- AI coding assistants that suggest and autocomplete code
- AI website builders that require less manual work
- AI SEO tools that optimize webpages and content
- AI marketing tools for generating ads, emails, social posts
As you can see, natural language processing (NLP) and language-based AI are being quickly adopted by businesses for all kinds of applications. But language is just one capability of generative AI. It has many other current and potential use cases beyond working with text.
Visual Art and Enhancement
Generative AI is really shaking things up when it comes to visual creativity and enhancement. With foundation models like Stable Diffusion, AI can now generate unique images and art just using text prompts. It's creating jaw-dropping artwork, realistic videos, and assisting with photo editing. Tools like Midjourney and Photoshop are leading the way in using this type of AI.
We've written a lot about the top AI tools for visuals. These include:
- AI design tools that create logos, graphics, illustrations, and more
- AI art generators that produce original artwork from text
- AI video generators that create realistic looking video clips
- AI photo enhancers that improve quality, upscale, and modify images
- AI image upscalers that increase resolution and sharpness
As you can see, generative AI is reshaping what's possible in terms of visual creativity and media production. The applications go far beyond just working with text and language. AI is unlocking new potential for generating and enhancing all kinds of digital media and visual content.
Audio Generation and Speech Processing
Generative AI is also transforming the world of audio. It can now generate music in whatever style you want. Or you can use it as a text-to-speech tool to convert written words into natural sounding speech. That makes content more accessible for visually impaired users. On the flip side, speech-to-text tools can transcribe audio files, making them searchable and easier to analyze.
Some of the top audio-focused AI tools are:
- AI voice generation tools that create realistic voices from text
- AI music creators that generate original songs, beats, and more
- AI text-to-speech tools that read text aloud naturally
In summary, generative AI is reshaping what's possible for working with audio, music, and speech. It can synthesize natural sounding voices, unique music, and accurately transcribe audio. This expands the potential for creating and consuming auditory content.
How does generative AI work?
Generative AI systems utilize a complex computational technique called deep learning to examine large datasets and identify common patterns and arrangements. This knowledge is then leveraged to create new and convincing outputs. The models accomplish this through the integration of machine learning methods known as neural networks. Neural networks loosely mimic how the human brain absorbs information over time and learns from it.
For example, by inputting vast quantities of fiction writing, over time a generative AI could recognize and recreate the core components of a story - plot structure, characters, themes, narrative tools, etc.
Generative AI models become more advanced the more data they ingest and produce. This continual enhancement stems from the foundational deep learning and neural network techniques. As these models generate more content, their outputs grow increasingly realistic and human-like. Through iterative learning, the systems gain strengthening linguistic and contextual awareness.
In summary, generative AI leverages computational methods like deep learning and neural networks to extract insights from large datasets. It then utilizes these learnings to create novel, convincing content that progresses in quality over time. This emerging technology holds much promise across many industries and applications.
How to Use Generative AI Responsibly
Generative AI has amazing potential with its ability to produce human-like content. But the power of this technology also brings up ethical issues and the risk for misuse. It's crucial that we address these challenges responsibly. That's the best way to tap into the full potential of generative AI while minimizing harm. Whether you're using consumer AI tools, building off a broader model, or creating your own, we all have a role to play in using AI ethically.
Beyond the doom-and-gloom predictions about AI, there are real but hard to define risks involved in using it.
The sky is not necessarily falling. But we do need to thoughtfully consider how to steer this technology in a direction that benefits society while protecting against potential downsides. If we want to enjoy the upsides of generative AI, it's on all of us to use it in a responsible and ethical way.
Inherent Risks and Criticisms
Like any powerful technology, generative AI comes with its own challenges and potential downsides. One big concern is that these AI models don't inherently fact check the information they generate. They might produce content based on inaccurate or misleading data, spreading false information as a result. Even worse, when they make a mistake, it's not always obvious that they did.
This is especially worrying for fields like journalism or academia where accuracy is crucial. Even in casual writing, AI can "hallucinate" or make up facts, especially when it struggles to complete its output.
Another risk is around content authenticity. As AI-generated content becomes more common, AI detection tools are being developed to flag it. Publishers or individuals using AI extensively could face major reputation damage, especially if the AI content isn't clearly labeled.
The key is being aware that generative AI doesn't have human judgment. It can inadvertently spread misinformation or plagiarize. We need to use these models responsibly and transparently. Fact checking and citing sources is still critical, even when AI is involved in creating content.
Examples of Generative AI
In 2023, generative AI has exploded in popularity largely thanks to breakthroughs like OpenAI's Chat GPT and DALL-E. Rapid progress in underlying technologies like natural language processing has also made generative AI accessible to consumers and creators.
Major tech firms have quickly jumped into the space, with Google, Microsoft, Amazon, Meta and more releasing their own generative AI tools within months.
While text and image models are well-known, there are numerous types of generative AI. Typically a user provides a prompt to guide the model to produce a desired output - whether text, images, video, music or otherwise.
Notable examples include:
- ChatGPT - An AI language model by OpenAI that generates human-like text responses to prompts.
- DALL-E 2 - Also by OpenAI, this model creates images and art from text descriptions.
- Google Bard - A generative AI chatbot rival to ChatGPT, powered by Google's PaLM language model.
- Midjourney - Developed by Midjourney Inc., this interprets prompts to generate images and art.
- GitHub Copilot - An AI coding assistant that suggests code completions.
- Llama 2 - Meta's open source language model for conversational AI like chatbots.
- xAI - A new generative AI company founded by Elon Musk after leaving OpenAI.
In summary, major progress in generative AI is enabling new creative tools and experiences across industries. But thoughtful governance remains vital as applications continue proliferating.
Wrapping Up
Generative AI is more than just a technological advancement; it serves as a catalyst for creativity, efficiency, and innovation. As we delve deeper into its potential, one fact becomes apparent: generative AI is not merely shaping our future; it is already an integral part of our present reality.





